Imagine making strategic decisions without fearing that your information might be incomplete, outdated, or worse, incorrect. This is the ideal scenario that data governance makes possible. In a corporate environment increasingly driven by information, data is no longer just an operational record but a valuable asset — and like any asset, it must be protected, managed, and optimized.
In Brazil, the combination of accelerated digital transformation and the requirements of the LGPD (General Data Protection Law) has made the topic even more urgent: it is not enough to simply store information; it is essential to ensure quality, security, and responsible use. Beyond legal requirements, research shows significant benefits for organizations that invest in governance — programs in this area deliver an average ROI of 315% over three years, and AI and machine learning initiatives are 83% more likely to succeed when supported by robust data governance.
With a well-defined data governance strategy, organizations gain clarity to act, reduce waste, and build trust with customers and partners. More than just a technological trend, it is a competitive differentiator capable of driving growth and innovation.
What is data governance and why is it essential?
Data governance is the set of policies, processes, responsibilities, and technologies that ensure the quality, security, privacy, and ethical use of information within an organization. Its main objective is to guarantee that data — regardless of its origin or format — is reliable, consistent, and accessible to the right people, at the right time, and in a secure manner.
In practice, governance defines who can access the data, how it should be stored, which quality standards must be followed, and how to ensure compliance with laws and regulations such as the LGPD in Brazil and the GDPR in Europe.
While data management focuses on day-to-day operational activities (such as collection, storage, and maintenance), data governance operates at a strategic level, creating the structure that guides and regulates these activities. It is like the difference between driving a car (management) and setting the traffic rules and maintenance practices that keep it safe and efficient (governance).
In recent years, the relevance of data governance has grown exponentially. Large organizations are implementing formal governance practices to support artificial intelligence and analytics projects — a trend driven both by the need for security and by the ambition to unlock the full potential of data as a strategic asset.
Objectives of data governance in organizations
The purpose of data governance is to transform data into a strategic resource capable of generating real business value. By organizing and standardizing the use of information, it creates an environment where decisions can be made based on reliable datarather than subjective perceptions. This increases both the accuracy and the agility of strategic actions.
Poorly managed information leads to wasted resources, duplicated efforts, and compliance failures that may result in fines. Data governance works to optimize processes, eliminate redundancies, and reduce legal and financial risks, while also creating a solid foundation for new technologies to be safely and scalably incorporated.
Pillars of Data Governance
For data governance to be effective, it must rely on clear foundations that guide every step, from data capture to its strategic use. These pillars serve as guidelines to ensure the quality, security, and reliability of information throughout its entire lifecycle.
1. Data Quality
Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, consistent, and up to date is the first step in avoiding flawed analyses. This involves validation, cleansing, and standardization processesthat reduce noise and errors that could compromise strategic decisions.
2. Security and Privacy
With cyber threats on the rise, governance must establish strict data protection policies, including access control, encryption, and regular audits. Compliance with regulations such as Brazil’s LGPD and international standards is a key part of this pillar.
3. Compliance
Data governance must ensure that the use of information is aligned with applicable laws and regulations. This reduces legal risks and protects the company’s reputation, especially in highly regulated industries such as finance and healthcare.
4. Availability and Accessibility
Data should be readily accessible to authorized users at the right time, in a fast and efficient manner. This requires modern, scalable infrastructurecapable of supporting queries without compromising the performance of critical systems.
5. Accountability and Clear Roles
Assigning specific responsibilities to individuals and teams is essential for governance to function properly. Each dataset should have an “owner” responsible for its integrity, updates, and security.
When well applied, these pillars create a robust structure that not only ensures the reliability of information but also enables the organization to innovate and quickly adapt to market changes.
Main Benefits of Data Governance for Companies
By establishing validation and standardization processes, data governance ensures more accurate analyses, avoiding decisions based on incomplete or incorrect information. This level of reliability strengthens strategic security and increases the credibility of the data used in reports and decision-making.
In addition, data governance contributes to reducing operational costs by eliminating redundancies, improving the organization of information, and decreasing the time spent searching for and processing data. With high-quality information available at the right time, managers can act more quickly and assertively,aligning decisions with corporate goals and market dynamics.
Another essential benefit is the strengthening of information security. Through access policies and continuous monitoring, governance reduces the risk of data breaches, cyberattacks, and misuse of sensitive information, protecting both the company and its customers.
This protection, combined with organization and reliability, creates fertile ground for innovation and digital transformation, since projects in artificial intelligence, machine learning, and big data require clean and well-structured data to succeed.
Finally, companies that master data governance achieve a sustainable competitive advantage. By fully trusting their information, they can react more quickly to trends, identify new opportunities, and position themselves in a differentiated way in the market.
In a scenario where information is as valuable as financial capital, governance acts as a value multiplier, ensuring that every decision is based on solid and reliable evidence.
Best Practices for Efficient Data Governance
For data governance to deliver consistent and sustainable results, it is necessary to adopt clear, well-documented methods that are fully integrated into the organization’s daily operations. These practices help ensure that governance policies are not just formal documents but routines embedded in the company’s culture.
1. Define Clear Policies and Processes
Establish objective rules for data collection, storage, access, updating, and disposal. Document each step and make sure all stakeholders understand the guidelines.
2. Create a Data Governance Committee
Form a multidisciplinary group with representatives from IT, information security, business areas, and compliance. This committee will be responsible for making strategic decisions and monitoring policy adherence.
3. Map Data Sources and Flows
Identify where data comes from, how it circulates within the organization, and which systems use it. This mapping is essential to detect bottlenecks, risks, and optimization opportunities.
4. Establish KPIs and Data Quality Metrics
Track indicators such as completeness, accuracy, consistency, and update frequency. This allows organizations to measure the impact of governance and justify investments.
5. Train and Engage Teams
Conduct periodic training sessions to raise awareness among all employees about the importance of governance and how to apply it in daily routines.
6. Automate Processes Whenever Possible
Use data catalog, integration, and data quality monitoring tools to reduce manual work and increase efficiency.
When applied consistently, these practices make data governance a central element of business strategy, strengthening security, compliance, and agility in decision-making.
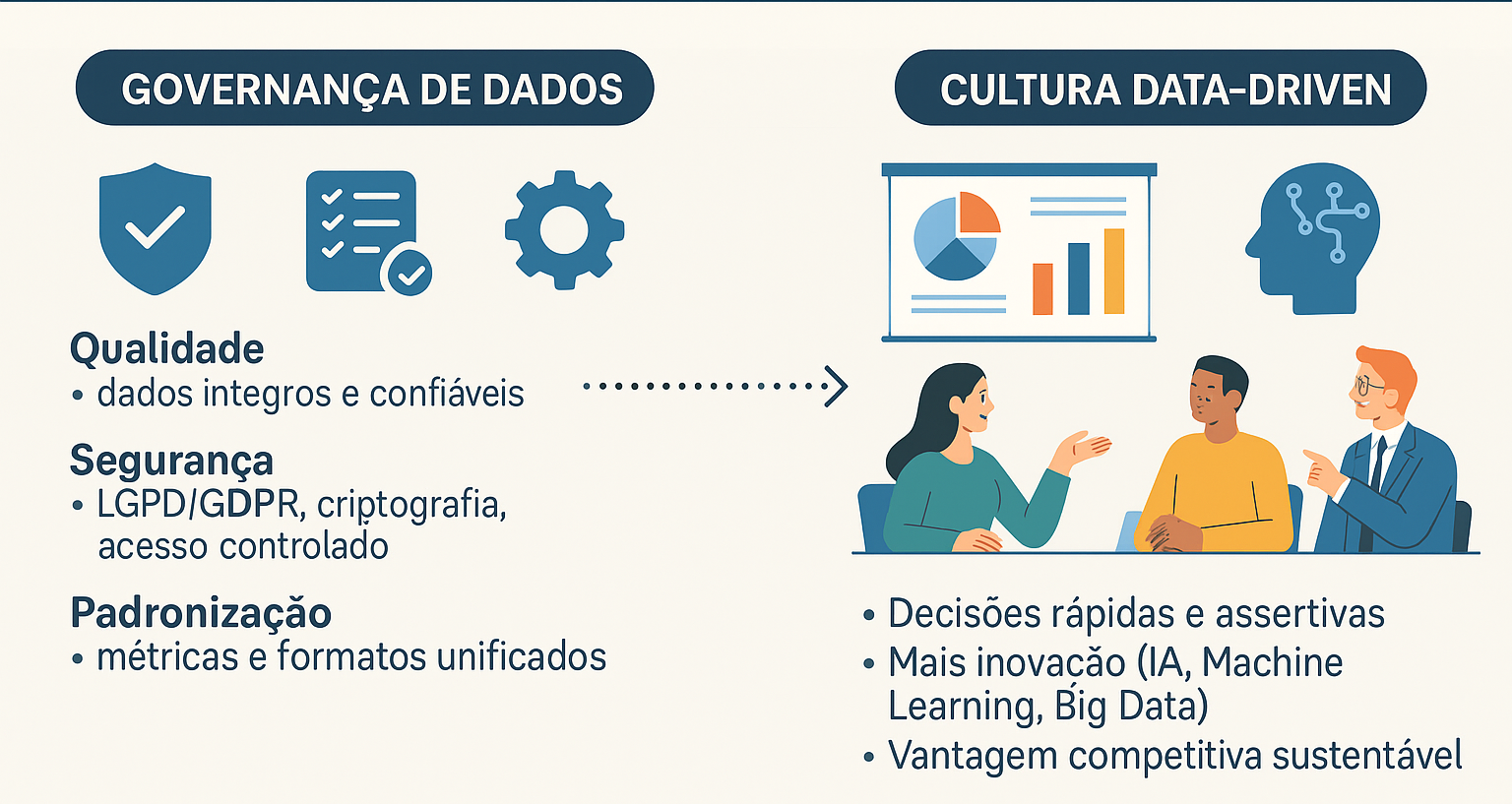
Data Governance and Data-Driven Culture
Data governance is the foundation of a data-driven culture — a management model in which decisions are made based on reliable data rather than intuition or experience. Without well-structured governance, companies run the risk of working with inconsistent, duplicated, or outdated information, undermining their entire analytics strategy.
In a data-driven environment, governance ensures that:
- The data used in analyses is accurate, complete, and up to date.
- Formats, metrics, and definitions are standardized across different business areas.
- Security and privacy are safeguarded, avoiding legal and reputational risks.
- Information is available to the right people at the right time, without operational bottlenecks.
According to McKinsey, companies that adopt a data-driven culture supported by solid governance are 23 times more likely to acquire customers, six times more likely to retain them, and 19 times more likely to be profitable.
Moreover, data governance drives innovation by creating a trusted environment for the use of technologies such as artificial intelligence, machine learning, and advanced analytics. When organizations trust their own data, they can fully unlock the potential of these solutions with both security and scalability.
In short, a data-driven culture relies on governance to exist sustainably. Without clear rules, defined roles, and standardized processes, data loses its strategic value and ceases to be a true competitive differentiator.